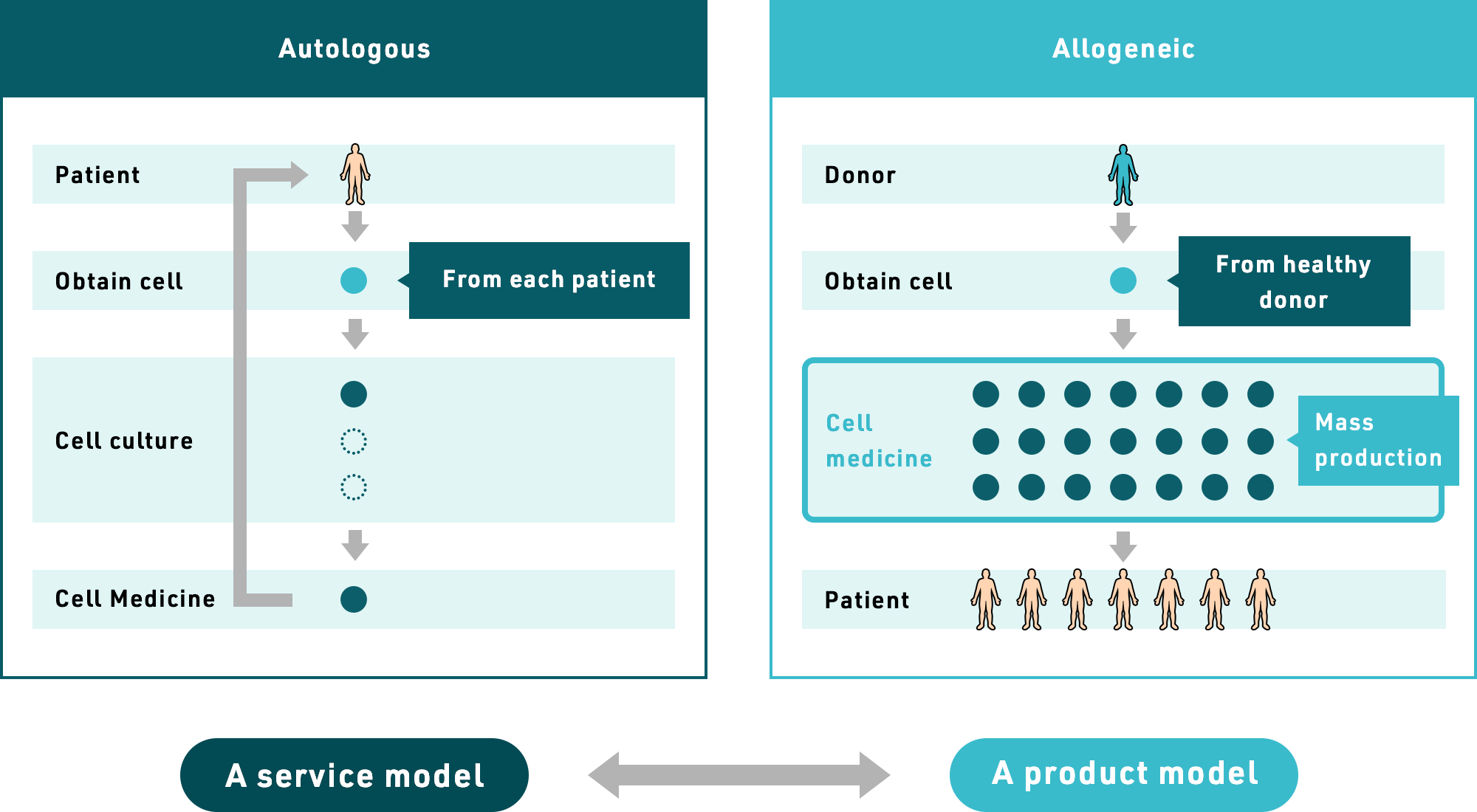
Cellular approaches to regenerative medicine can be broadly categorized as either autologous or allogeneic.
Autologous cell treatment involves a procedure in which the patients’ own cells are removed, processed, and then used as a treatment. While this process is frequently used, it has serious drawbacks. For example, a prodigious commitment of time and effort is required to process cells separately for each individual patient and this often results in uneven quality of cells across different patients. It is also very costly.
Conversely, in allogeneic cell treatment, patients receive cells collected from a healthy cell donor. These cells are cultured in large quantities and processed to become medicines with uniformly high quality. Thus, using allogeneic cells, a superior therapy can be made available to patients at greatly reduced cost.
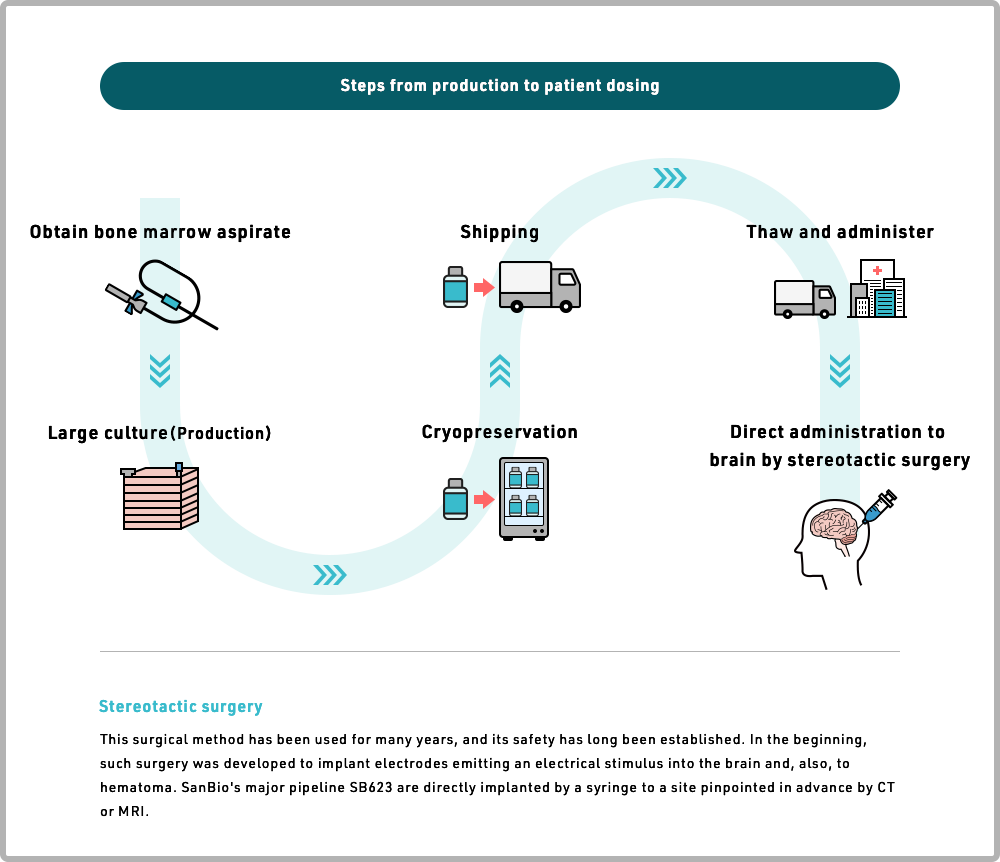
SanBio's allogeneic Cell Therapy Medicine (MSC implantation), using cells from a small number of healthy adult donors. We culture mesenchymal stem cells isolated from bone marrow from these donors, resulting in a manufactured, homogenous final product. We then transport this cryopreserved product to hospitals. The product is then administered to patients after thawing.
Thus, patients can expect that SanBio products will be readily available and will not require long delays and additional procedures required for processing a patient's own bone marrow.